By Franklin Cook
The special report "Systems Must Include Three Levels of Care for Aftermath of Suicide" (available to read or download below) is essential reading for anyone involved in developing, implementing, or assessing services designed to help people who have been affected by a suicide fatality, such as first responders, mental health practitioners, and the suicide bereaved.
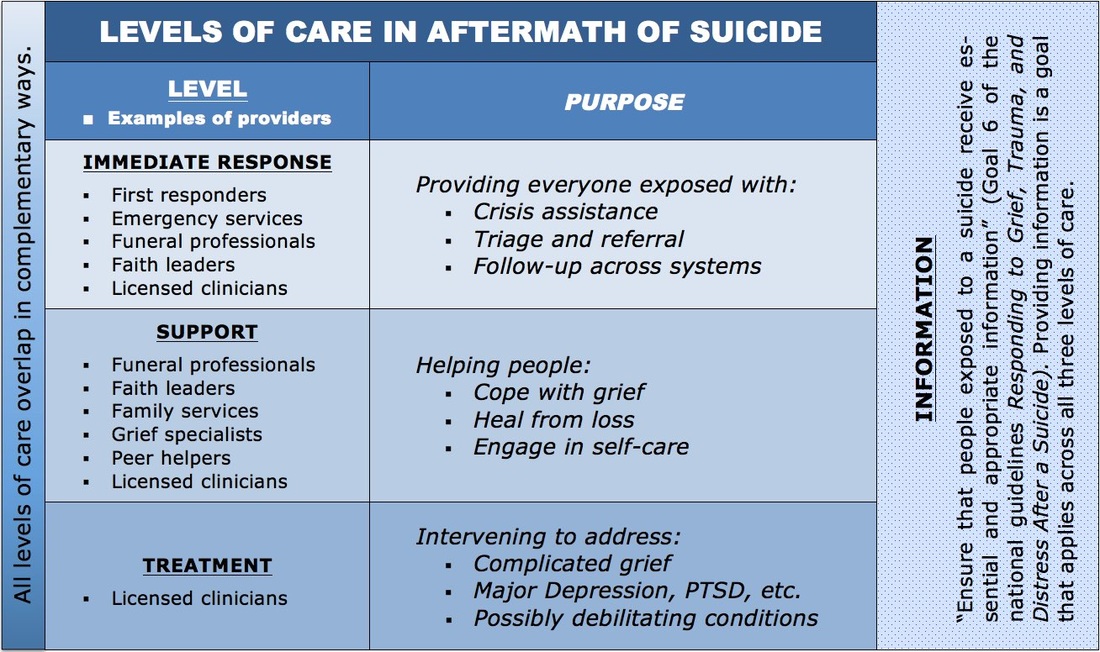
Based on recently released national guidelines,* the report delineates three levels of care:
• Immediate response: crisis assistance, triage and referral, follow-up
• Support: assistance with grief and loss, self-help
• Treatment: interventions for potentially debilitating conditions
Quoting Goal 6 of the guidelines -- which is to "ensure that people exposed to a suicide receive essential and appropriate information" -- the report explains that providing such information is a goal that applies across all three levels of care. It also features an addendum, "Information for People Exposed to a Suicide" that outlines the kinds of information that are valuable to people exposed to a suicide and points to the online resource directory available at bit.ly/afterasuicide.



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed